Red Hat Virtualization
General
For RHV 4+ environments, you can use API v4 for invoking all backup-related tasks.
Import/export mode defines the way the backups and restores are done. Red Hat Virtualization (with API v4) supports the following modes:
Disk attachment, which exports VM metadata (in OVF format) with separate disk files (in RAW format) via the Proxy VM with the Node installed.
incremental backup with a generic mechanism
proxy VM required in each cluster - used for the disk attachment process
Disk image transfer, which exports VM metadata (in OVF format) with disk snapshot chains as separate files (QCOW2 format):
supports incremental backup using deltas
disk images are transferred directly from API (no Proxy VM required)
Change Block Tracking, this method backup only blocks with changes and skip zeroed sectors.
supported since 4.4 (with Libvirt 6+, qemu-kvm 4.2+ and vdsm 4.40+)
supports incremental backup using the dedicated CBT API
Note: When using backup APIs - Red Hat highly recommends updating the RHV environment to the most recent version (4.4 - at the time of writing) - refer to this article for more information.
When adding RHV 4.0+ hypervisor managers, use a URL similar to the following:
https://RHV_MGR_HOST/ovirt-engine/apiNote: a username for RHV environments needs to be provided in the user@domain format - for example admin@internal. This user must have all permissions related to managing snapshots, creating/removing VMs, operating disks, and exporting data.
Backup Strategies
Red Hat Virtualization environments can be protected in several ways.
Note: Different strategies require a node to be installed either as a VM on the environment that you back up or installed separately.
Note: All live snapshots are attempted with quiescing enabled. If the snapshot command fails because there is no compatible guest agent present, the live snapshot is re-initiated without the use-quiescing flag.
Disk attachment with Proxy VM
In this strategy, you have a VM called “Proxy VM” that invokes commands on your hypervisor manager to snapshot and attach drives of a specific VM to itself (Proxy VM). The Proxy VM is able to read the data from the attached disk snapshots and forward them to the backup provider.
This strategy allows you to exclude drives from the backup that you do not need. Remember that you need to install 1 Proxy VM per cluster so that the drives the node tries to attach are reachable.
Drawback - no incremental backup for now.
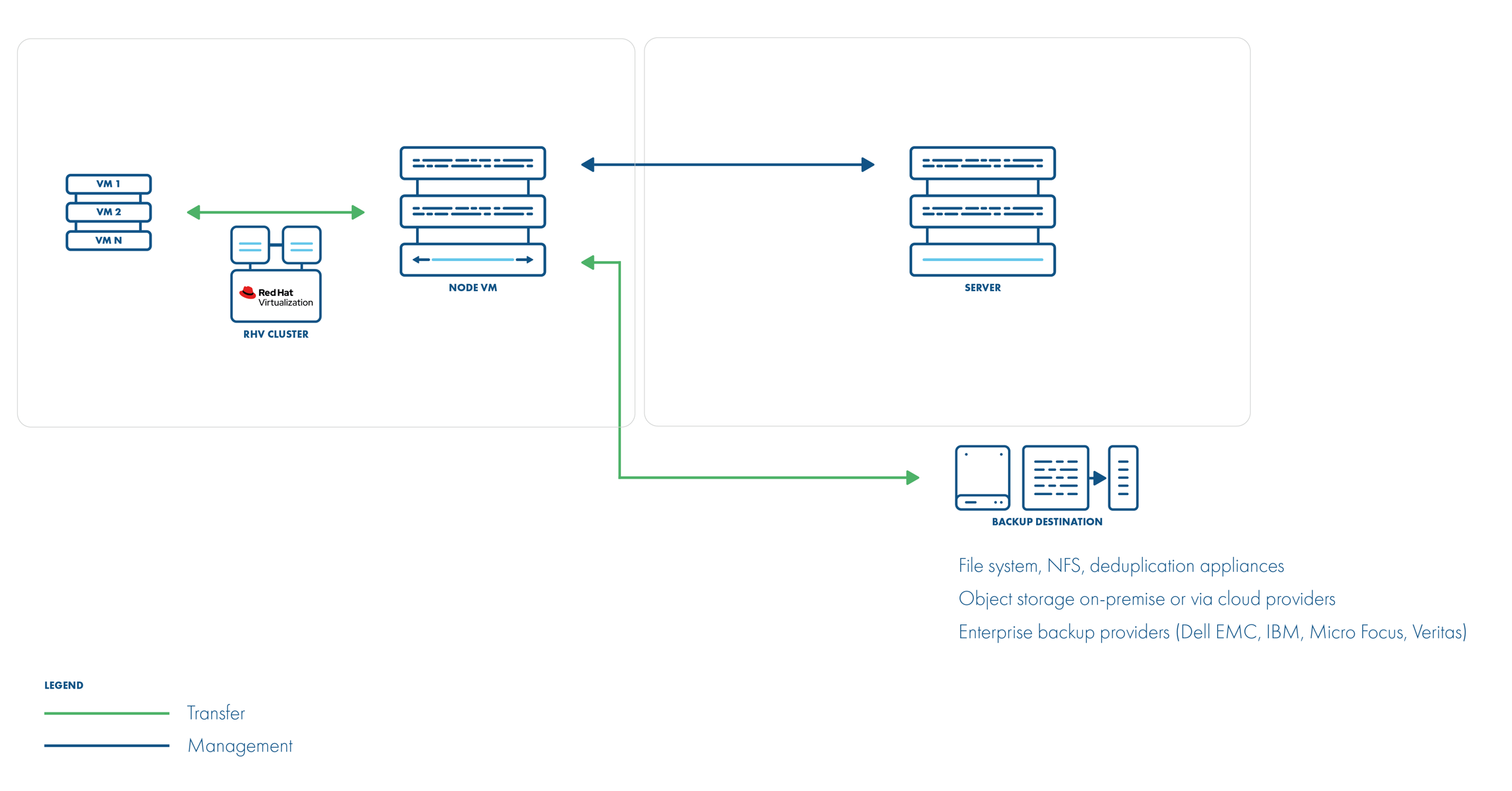
Backup Process
crash-consistent snapshot using hypervisor's API
optionally FS freeze can be executed before snapshot can be executed (FS thaw once the snapshot is completed) if enabled and guest tools installed inside
optional application consistency using pre/post snapshot command execution
metadata exported from API
snapshot disks are mounted one by one to the Proxy VM
data read directly on the Proxy VM
incremental backups are not supported
restore creates empty disks on the Proxy VM, imports merged data then recreates VM and reattaches volumes to the target VM
Note: RHV API v4 environments require Storware Backup & Recovery Node to be installed in one of the VMs residing on the RHV cluster. Storware Backup & Recovery should automatically detect the VM with Storware Backup & Recovery during the index operation.
Disk attachment mode requires Virtio-SCSI to be enabled on the Storware Backup & Recovery Node VM (which can be enabled in VM settings -> Resource Allocation -> VirtIO-SCSI Enabled at the bottom).
During backup/restore operations, disks are transferred by attaching them to the proxy VM. This approach does not require an export storage domain to be set up.
Make sure that you follow these steps: LVM setup on Storware Backup & Recovery Node for disk attachment backup mode.
Disk image transfer API
This API appears in RHV 4.2 and allows the export of individual snapshots directly from the RHV manager. So instead of having to install multiple Proxy VMs, you can have a single external Node installation, which just invokes APIs via the RHV manager.
This strategy supports incremental backups. Assuming you have RHV 4.2 or newer – just add your manager to Storware Backup & Recovery and setup is done. From a network perspective, it requires two additional ports to be open - 54322 and 54323 - and your data to be pulled from the hypervisor manager.
Unfortunately, there are a few problems with the current architecture of this solution. The biggest issue is that all traffic passes via the RHV manager, which may impact the transfer rates that you can achieve during the backup process. To put this into perspective – in disk attachment, you can basically read data as if it is a local drive, where it could potentially be deduplicated even before transferring it to the backup destination.
Note: From RHV version 4.4.3, data is transferred directly from/to hosts.
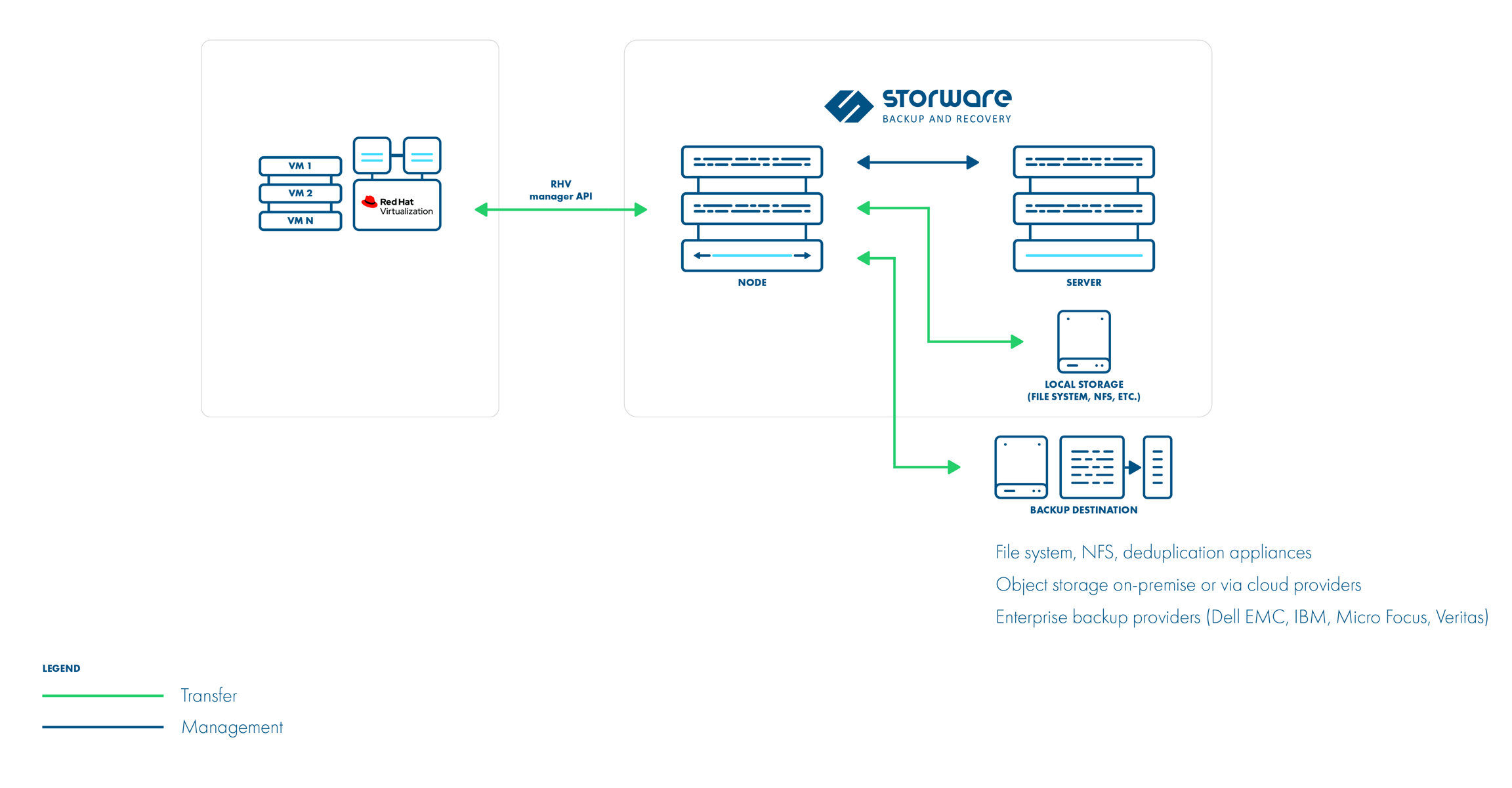
Backup Process
crash-consistent snapshot using hypervisor's API
optionally FS freeze can be executed before snapshot can be executed (FS thaw once the snapshot is completed) if enabled and guest tools installed inside
optional application consistency using pre/post snapshot command execution
metadata exported from API
data transfer initiated on the manager and actual data exported from the hypervisor using imageio API
incremental backups use the same APIs, but requests for changed blocks only
the last snapshot kept on the hypervisor for the next incremental backup (if at least one schedule assigned to the VM has a backup type set to incremental)
restore recreates VM from metadata using API and imports merged chain of data for each disk using imageio API
Disk image transfer mode exports data directly using RHV 4.2+ API. There is no need to set up an export storage domain or set up an LVM. This mode uses snapshot chains provided by RHV.
You may need to open communication for the additional port 54323 on the RHV manager and 54322 on the RHV hosts - it needs to be accessible from Storware Backup & Recovery Node. Also, make sure that your ovirt-imageio-proxy services are running and properly configured (you can verify this by trying to upload images with RHV UI).
Follow the steps in this section: Full versions of libvirt/qemu packages installation.
Change Block Tracking
This is a new method that is possible thanks to changes in RHV 4.4. It uses information about zeroed and changed blocks to reduce data size and make the process faster.
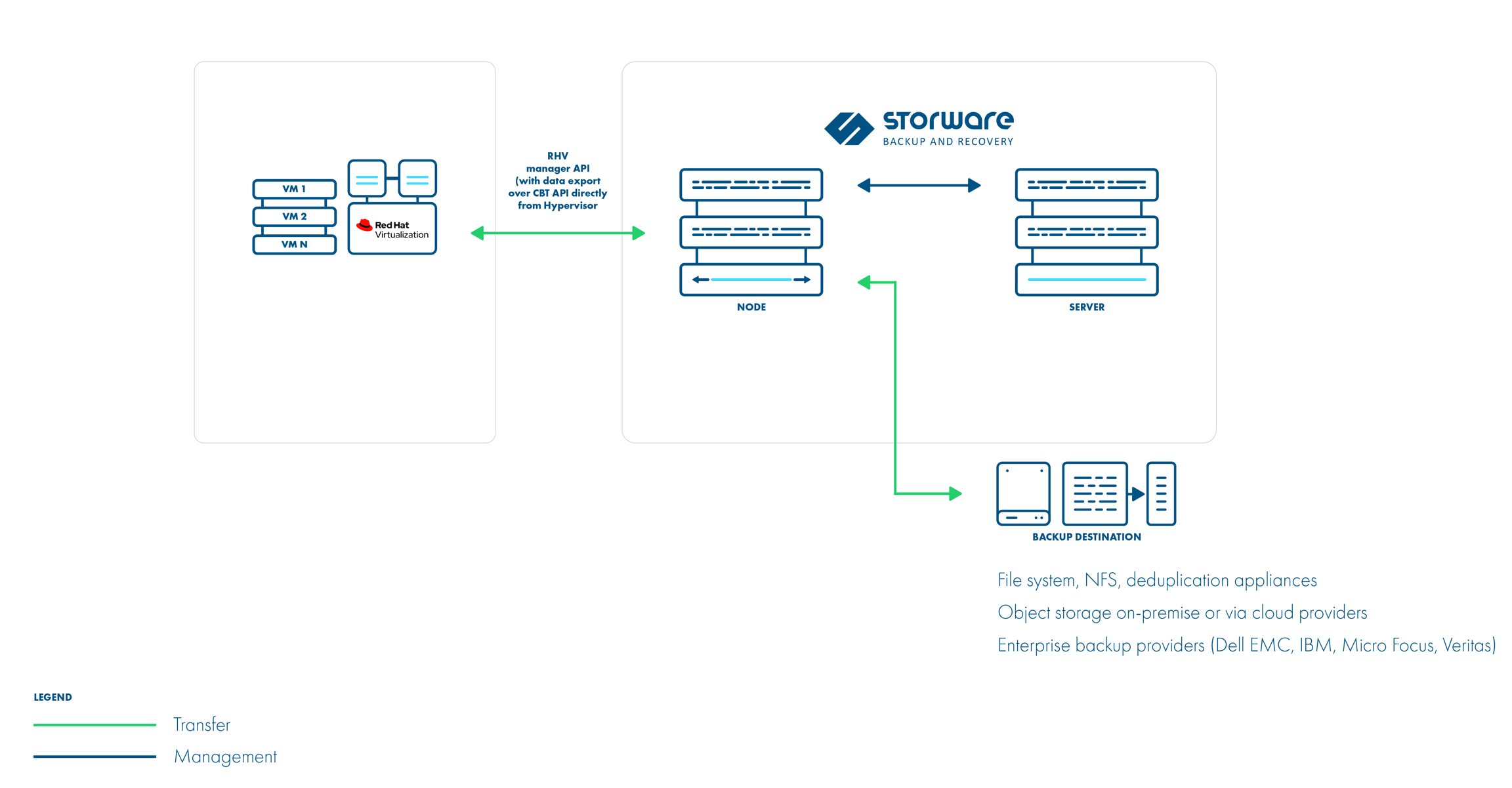
This strategy supports incremental backups.
The QCOW2 format is required for incremental backups so that disks enabled for incremental backup use the QCOW2 format instead of the raw format.
Also, this strategy doesn't need snapshots in the backup process. Instead, every incremental backup uses a checkpoint that is a point in time that was created after the previous backup.
Instant restore
To use an instant restore feature, backup destination from which VM will be restored, has to be of a synthetic type. The restore process creates a NFS share on the Storware Backup & Recovery node, later this share is attached to the RHV as a new storage domain. Then it creates a new virtual machine and attaches the disks from the newly created storage domain to it. To use instant restore you have to click the restore button in the instances list and choose the option instant restore.

Live migration
You can enable the live migration option during instant restore. It will automatically start the disks migration to the chosen storage after the VM is restored and powered on.
Supported features
Supported backup strategies: Disk attachment, Image transfer, CBT (preferred)
Supported versions
4.4
4.4
4.4
The last snapshot is kept on the hypervisor for incremental backups
No
Yes
No
Access to hypervisor OS required
No
No
No
Proxy VM required
Yes
No
No
Full backup
Supported
Supported
Supported
Incremental backup
Not supported
Supported
Supported
Synthetic backups
Supported
Supported
Supported
File-level restore
Supported
Supported
Supported
VM disk exclusion
Supported
Supported
Supported
Quiesced snapshots
Supported
Supported
Supported
Snapshots management
Supported
Supported
Supported
Pre/post command execution
Supported
Supported
Supported
Access to VM disk backup over iSCSI
Supported
Supported *
Supported
VM name-based policy assignment
Supported
Supported
Supported
VM tag-based policy assignment
Supported
Supported
Supported
Power-on VM after restore
Supported
Supported
Supported
* Only for RAW disk types
Network requirements
Disk attachment
Connection URL: https://MANAGER_HOST/ovirt-engine/api
Node
oVirt/RHV/OLVM manager
443/tcp
oVirt/RHV/OLVM API access
Disk Image Transfer
Connection URL: https://MANAGER_HOST/ovirt-engine/api
Node
oVirt/RHV/OLVM manager
443/tcp
oVirt/RHV/OLVM API access
Node
oVirt/RHV/OLVM hypervisor
54322/tcp
oVirt/RHV/OLVM ImageIO services - for data transfer (primary source)
Node
oVirt/RHV/OLVM manager
54323/tcp
oVirt/RHV/OLVM ImageIO services - for data transfer (fallback to ImageIO Proxy)
Change-Block Tracking
Connection URL: https://MANAGER_HOST/ovirt-engine/api
Node
oVirt/RHV/OLVM manager
443/tcp
oVirt/RHV/OLVM API access
Node
oVirt/RHV/OLVM hypervisor
54322/tcp
oVirt/RHV/OLVM ImageIO services - for data transfer
Node
oVirt/RHV/OLVM manager
54323/tcp
oVirt/RHV/OLVM ImageIO services - for data transfer
Last updated