OpenStack
Overview
Storware Backup & Recovery supports backup for OpenStack:
Disk attachment through Cinder with generic incremental (preferred):
supports all hypervisors and storages
supports incremental backup
proxy VM is required - used for the disk attachment process.
Disk image transfer - for KVM hypervisors with VMs using QCOW2
Volumes or Ceph-based storage:
supports incremental backup
disk images are transferred directly from API (no Proxy VM required)
Disk attachment through Cinder:
supports all hypervisors and storages
no incremental backup
proxy VM is required - used for the disk attachment process.
Backup Strategies
Libvirt strategy
Storware Backup & Recovery supports OpenStack environments that use KVM hypervisors and VMs running on QCOW2 or RAW files. Storware Backup & Recovery communicates with OpenStack APIs such as Nova and Glance to collect metadata and for the import of the restored process. However, the actual backup is done over SSH directly from the hypervisor. Storware Backup & Recovery Node can be installed anywhere - it just needs to have access to the OpenStack APIs and hypervisor SSH via a network. Both full and incremental backups are supported.
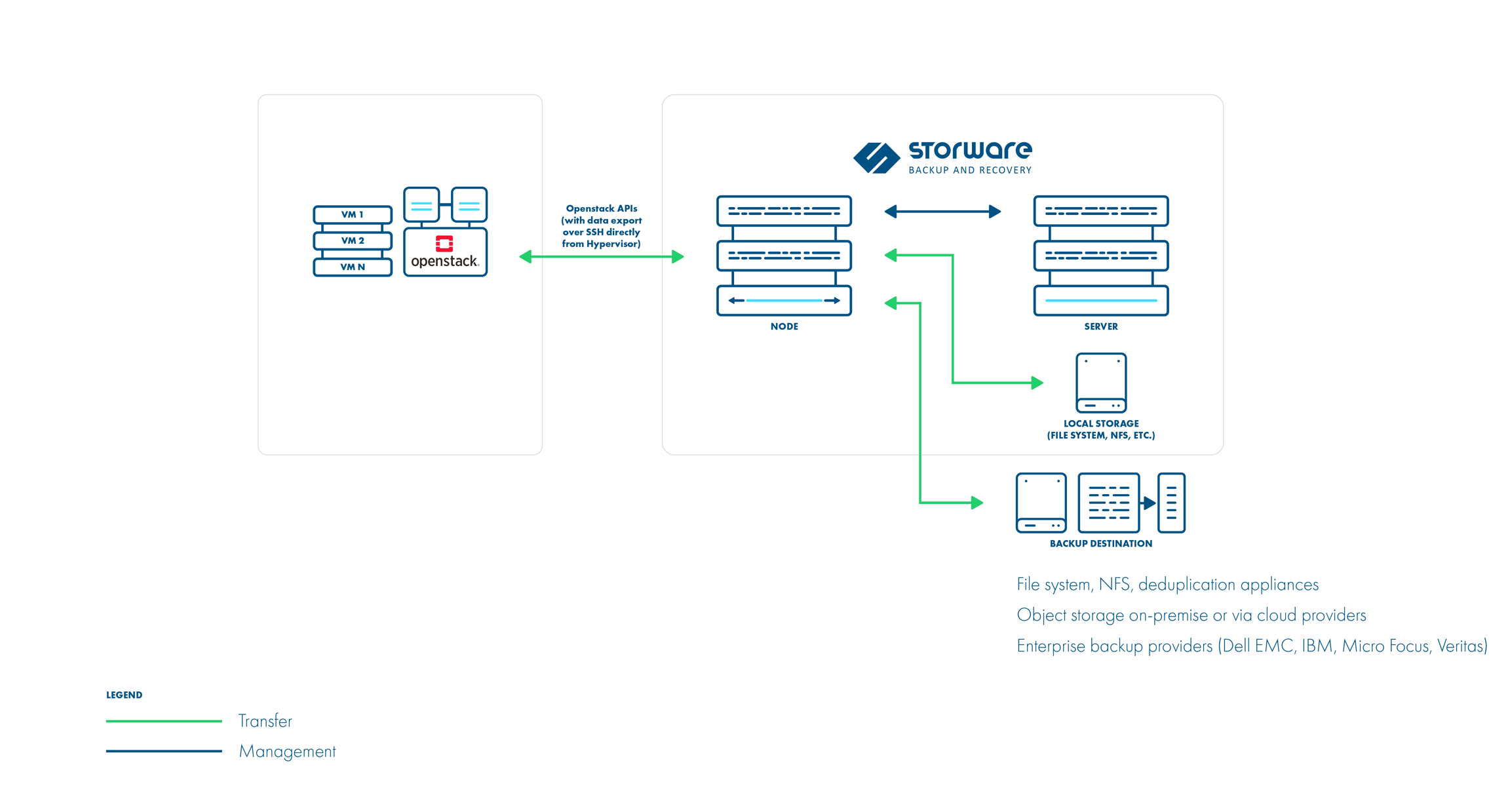
Backup process:
direct access to the hypervisor over SSH
crash-consistent snapshot taken directly using virsh (QCOW2/RAW file), rbd snapshot for Ceph (separate call for each storage backend)
optional application consistency using pre/post snapshot command execution • QCOW2/RAW-file data exported over SSH (optionally with netcat)
Ceph RBD data exported using rbd export or RBD-NBD when incremental is used
metadata exported from OpenStack APIs (nova, glance, cinder)
the last snapshot kept on the hypervisor for the next incremental backup (if at least one schedule assigned to the VM has backup type set to incremental)
restore recreates files/volumes according to their backend (same transfer mechanism as used in backup) and then defines VM on the hypervisor
Disk attachment
Storware Backup & Recovery also supports the disk-attachment method using cinder. This should allow you to use cinder-compatible storage and still allow Storware Backup & Recovery to create backups. Incremental backup is supported in disk attachment changed block tracking (which has higher CPU overhead). Storware Backup & Recovery needs to communicate OpenStack service's API to attach drives to the proxy VM with Storware Backup & Recovery Node installed.
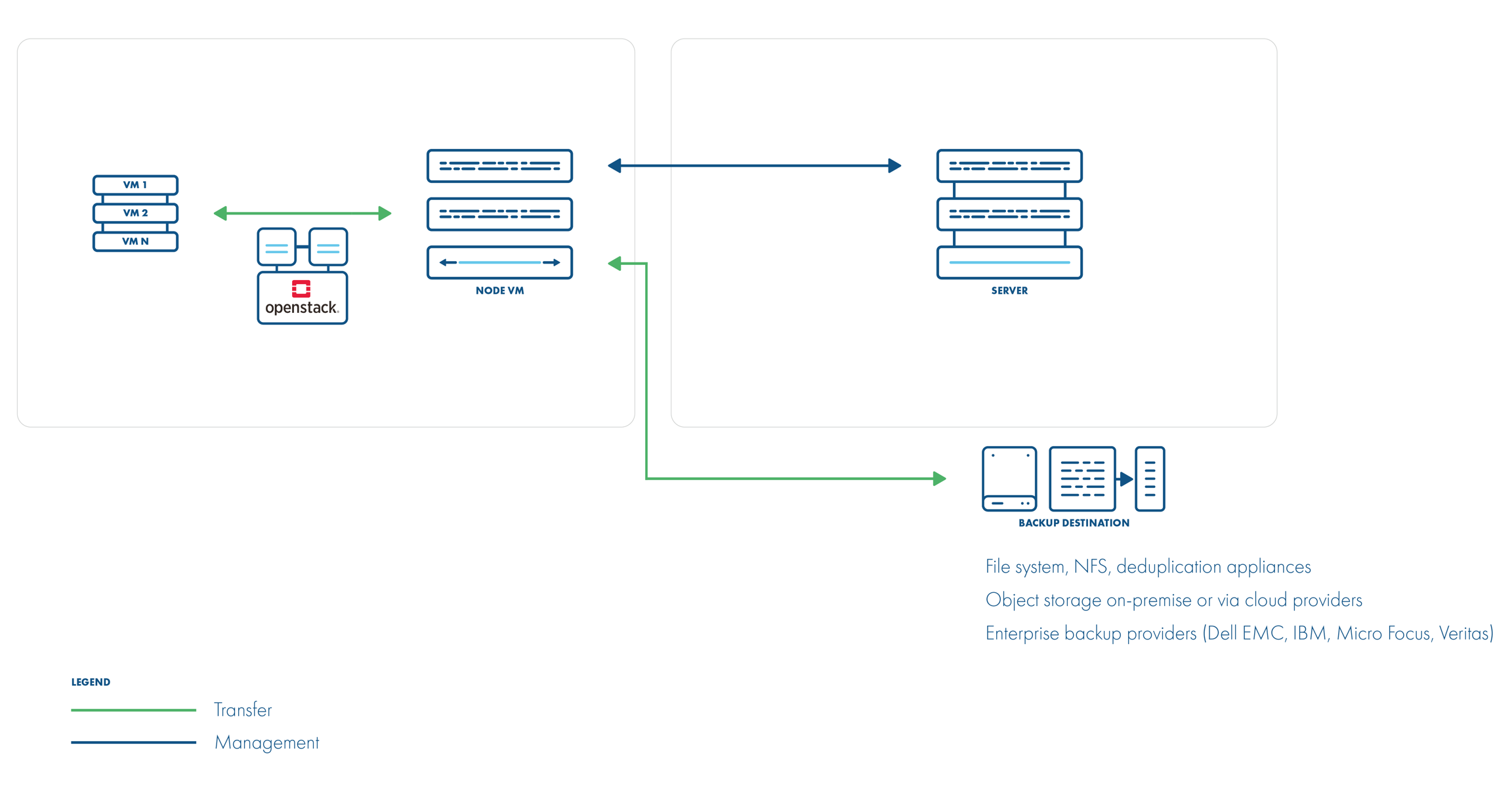
Backup process:
crash-consistent snapshot using cinder API
optional application consistency using pre/post snapshot command execution
metadata exported from API
volumes created from snapshotted disks are mounted one by one to the Proxy VM
data read directly on the Proxy VM
incremental backups supported for Ceph RBD - a list of the changed blocks are fetched from the monitors, and only these blocks are read from the attached disk on the Proxy VM
if an instance is created from the glance image and "download image from glance" option is enabled data is downloaded from glance API, an instance is created from the instance metadata, and the images which are fetched from the glance API
restore creates empty disks on the Proxy VM, imports merged data then recreates the VM using these volumes, it will try to use the image from a glance if present in the target environment or it will upload the image to the glance and register it with the restored VM
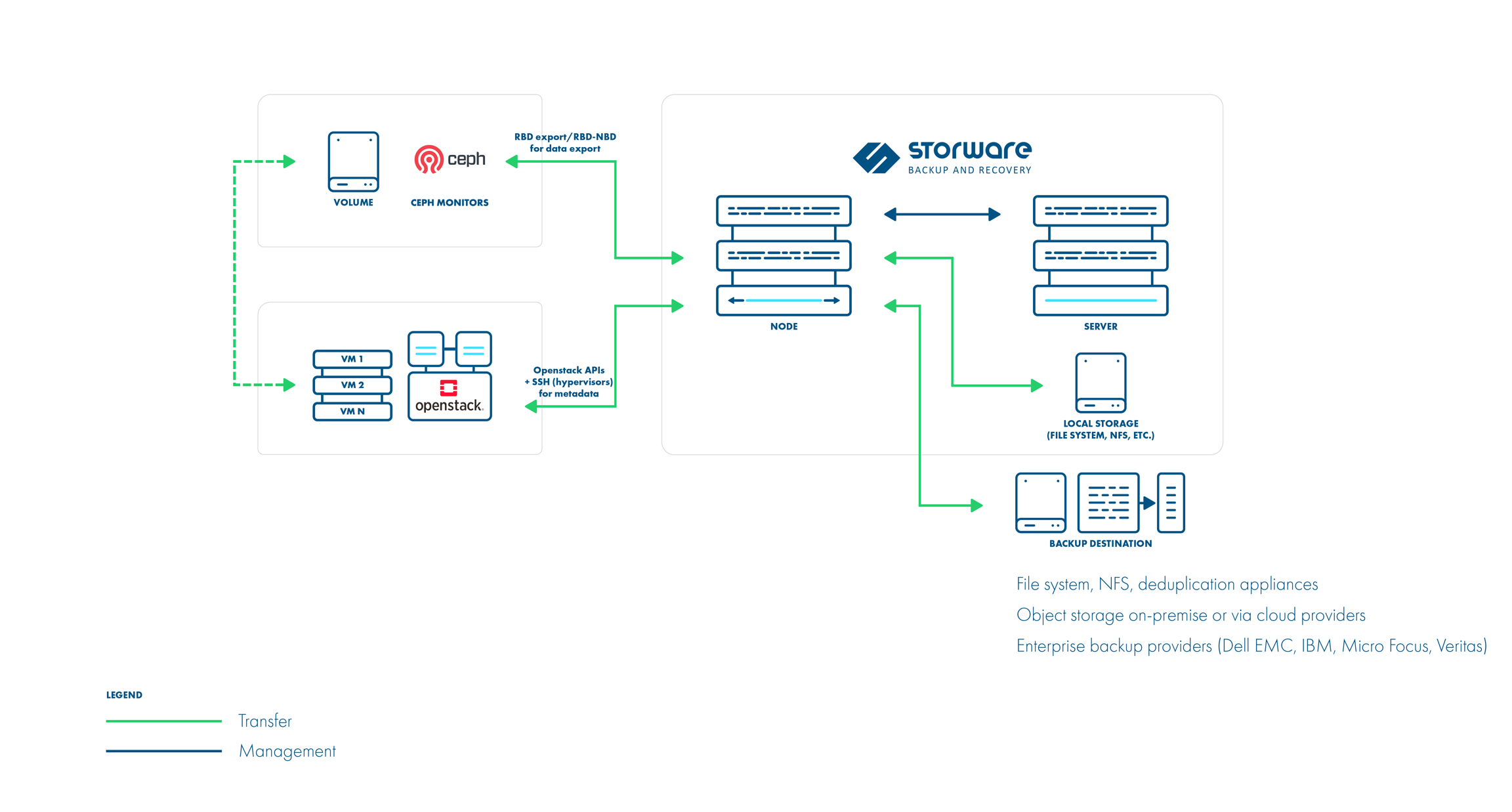
Ceph RBD storage backend
Storware Backup & Recovery also supports deployments with Ceph RBD as a storage backend. Storware Backup & Recovery communicates directly with Ceph monitors using RBD export/RBD-NBD when used with the Libvirt strategy or - when used with the Disk-attachment method - only during incremental backups (snapshot difference).
Libvirt strategy
Disk attachment strategy
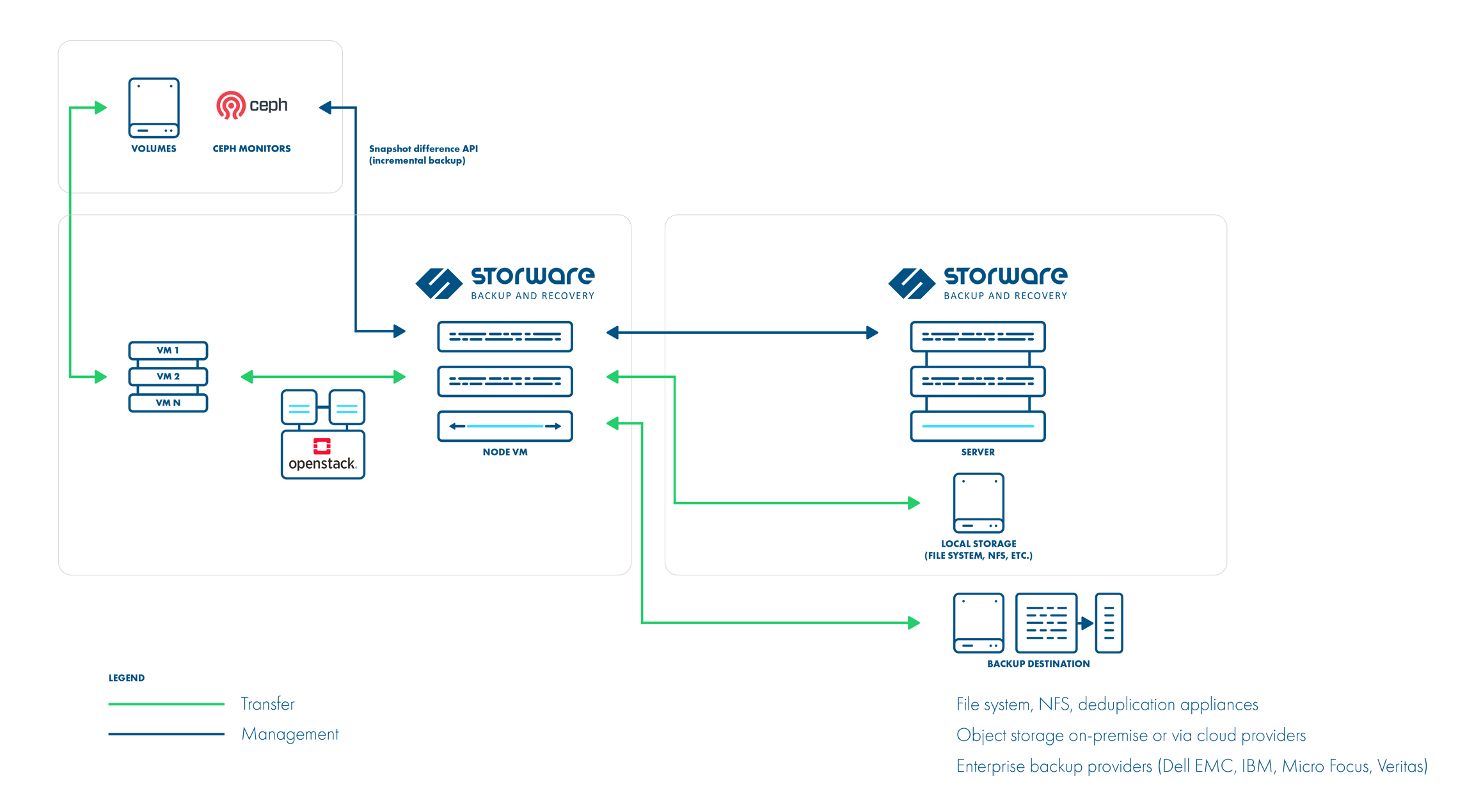
Example
Here is an example of a typical (expected) section that needs to be added in cinder.conf for Ceph in the OpenStack environment:
A good article on how to set up Ceph with OpenStack can be found here.
To set up the Openstack HVM with Ceph RBD volumes in Storware Backup & Recovery:
Add Ceph storage as described here
Add the hypervisor manager as described here.
Go to
Virtual Environments->Infrastructure->Clustersand select cluster that is used by Openstack.
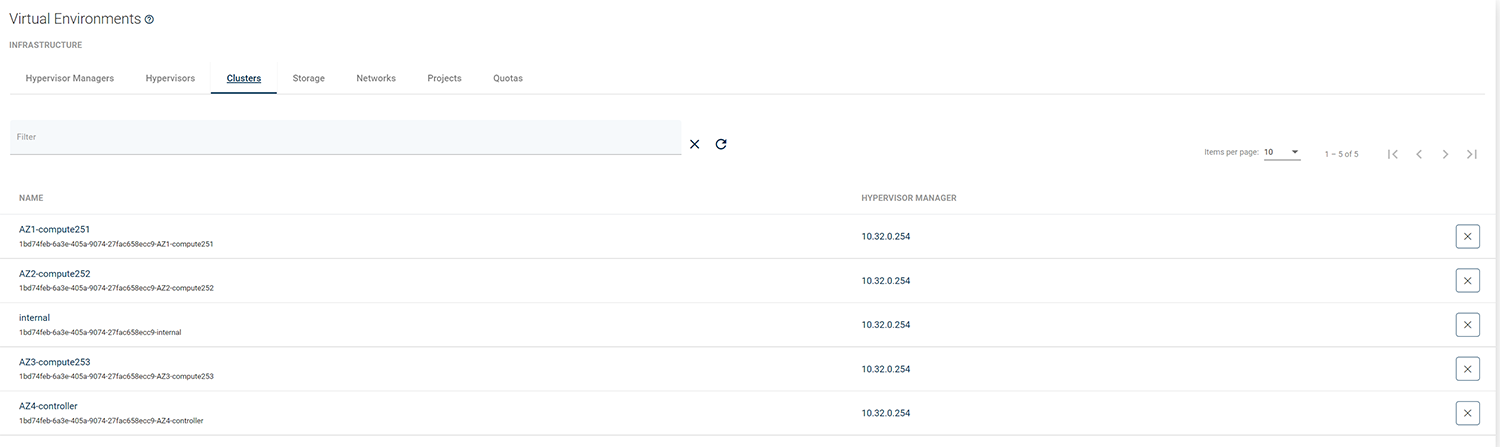
In
Storage Providerfield select previously added Ceph storage.
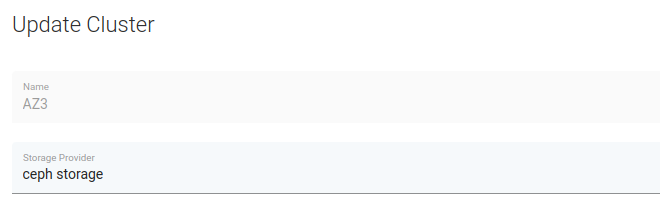
Now you can save and sync the inventory - if Ceph communication works properly you should be able to see Hypervisor Storage entries (in Hypervisors -> Storage tab) representing your Ceph storage pools.
Supported features
Supported backup strategies: Disk attachment (preferred), Image transfer, with generic incremental (preferred, if Ceph monitors are not accessible)
Supported versions
Wallaby, Xena, Yoga, Zed, Antelope, Bobcat, Caracal, Dalmatian, Epoxy
Wallaby, Xena, Yoga, Zed, Antelope, Bobcat, Caracal, Dalmatian, Epoxy
Wallaby, Xena, Yoga, Zed, Antelope, Bobcat, Caracal, Dalmatian, Epoxy
The last snapshot is kept on the hypervisor for incremental backups
Yes
No
Yes
Access to hypervisor OS required
No
No
Yes
Proxy VM required
Yes
Yes
No
Full backup
Supported
Supported
Supported
Incremental backup
Supported *
Supported
Supported *
Synthetic backups
Supported
Supported
Supported
File-level restore
Supported
Supported
Supported
VM disk exclusion
Supported
Supported
Supported
Quiesced snapshots
Not supported
Not supported
Not supported
Snapshots management
Supported **
Supported **
Not supported
Pre/post command execution
Supported
Supported
Supported
Access to VM disk backup over iSCSI
Supported
Supported
Supported ***
VM name-based policy assignment
Supported
Supported
Supported
VM tag-based policy assignment
Supported
Supported
Supported
Power-on VM after restore
Not supported (always on)
Not supported (always on)
Not supported (always on)
* Ceph RBD volumes only ** Without snapshot revert *** Ceph RBD/RAW disks only
Network requirements
Disk attachment
Connection URL: https://KEYSTONE_HOST:5000/v3
Node
Keystone, Nova, Glance, Cinder, Neutron
ports that were defined in endpoints for OpenStack services
API access to the OpenStack management services - using endpoint type that has been specified in hypervisor manager details
Node
Ceph monitors
3300/tcp, 6789/tcp
if Ceph RBD is used as the backend storage - used to collect changed-blocks lists from Ceph
SSH transfer
Connection URL: https://KEYSTONE_HOST:5000/v3
Note: you also must provide SSH credentials to all hypervisors that have been detected during inventory sync
Node
Hypervisor
22/tcp
SSH access
Hypervisor
Node
netcat port range defined in node configuration - by default 16000-16999/tcp
optional netcat access for data transfer
Node
Ceph monitors
3300/tcp, 6789/tcp, 10809/tcp
if Ceph RBD is used as the backend storage - used for data transfer over NBD
QCOW2 files on NFS storage
Example: scenario QCOW2 files residing on NFS
You can configure the NFS volume backend here:
https://docs.openstack.org/cinder/rocky/admin/blockstorage-nfs-backend.html
Make sure the QCOW2 volumes are enabled.
For an NFS backend, it's recommended to set these values in /etc/cinder/cinder.conf:
Nova volumes
Storware Backup & Recovery can back up Nova volumes using a libvirt (SSH transfer) strategy, which requires direct access to the hypervisor. The image from which the OS has been booted (without the changes made after instance creation), can also be protected - for more information, check out the Download image from glance option description in the OpenStack section.
Authentication Domains
Storware Backup & Recovery supports OpenStack environments with multiple domains. Each OpenStack Hypervisor Manager needs to have at least one Authentication Domain provided.
Storware Backup & Recovery supports two types of domain authorization:
Unscoped - single credentials to multiple domains
Scoped - single credentials to single domain
Single credentials to single domain
Scoping VMs to Domain option needs to be turned on.
In that setup user can create Authentication Domains for every Domain in OpenStack environment. Projects and Virtual Machines are only scanned in provided Authentication Domains.
Single credentials to multiple domains
Scoping VMs to Domain option needs to be turned off.
In that setup user need to create only one Authentication Domain. Projects and Virtual Machines are scanned in every domain that provided user has access to.
Tags
Tags in Nova are also scanned (when nova API ≥ 2.26). Tags can later be used in the auto-assignment of the backup policy.
Tags themselves are not part of the backup.
You can list tags for a specific instance in the OpenStack using this command:
Access Keys
During Inventory Synchronization, Storware Backup & Recovery scans all Keypairs (to which a user has access) and lists them as Access Keys. Access keys are not exported during backup. When restoring the instance, in the restore modal -> Advanced tab, the user can specify the Access Key (otherwise, the instance will be restored without one).
Flavors
During Inventory Synchronization, Storware Backup & Recovery scans all Flavors and saves their configuration. When restoring an instance, in the restore modal -> Advanced tab, the user can specify the flavor.
When restoring to a different OpenStack than the original instance was backed up, or the nova version is higher than 2.46 (where flavor ID cannot be fetched from the nova API) - you always need to specify in the restore modal -> Advanced tab which flavor should be used for recovery.
https://docs.openstack.org/api-ref/compute/?expanded=show-server-details-detail#show-server-details
Limitations
Storware Backup & Recovery does not backup and restores keypairs that user used in Storware Backup & Recovery doesn't have access to. The restored instance will have no keypairs assigned. In such a case, the keypairs have to be backed up and restored manually under the same name before restoring the instance.
For the libvirt strategy only, QCOW2/RAW files or Ceph RBD are supported as the backend.
The disk attachment method with Ceph requires access to the monitors from the Proxy VM.
General configuration
This section describes advanced setup. We recommend following this guide to configure more sophisticated environments. The wizard-based configuration (accessible from the dashboard) is suitable for simple PoC deployments, where the server and node are already installed as a proxy VM.
Go the Virtual Environments -> Virtualization Providers and click Create
Select OpenStack at the top
In the General tab:
specify Node configuration for the nodes communicating with the keystone
later you can override these settings on the Hypervisor level, but for now, select node config that is able to communicate with your OpenStack KeyStone
if using the disk attachment method, it has nodes residing in their corresponding Proxy VMs
URL - Keystone API URL, e.g.
https://10.201.32.40:5000/v3Region - provide the name of your region (each region must be added as a separate hypervisor manager
Choose import/export mode - this is backup strategy discussed in Backup Strategies section
Trust certificates - if you're using certificates that may not be trusted by you nodes - e.g. self-signed - you can enable this toggle. By default they will be imported automatically when connecting for the first time anyway.
In the OpenStack settings tab:
Endpoint interface type - interface type used to connect to the OpenStack services' endpoints returned from your Keystone
Download image from glance:
when enabled - this setting only applies when OS (boot) volume is either:
nova volume
cinder volume from image
the image will be downloaded only if the OS (boot) volume is not excluded.
this setting will download the OS image from glance instead of the OS (boot) volume
this means that changes applied to the OS (boot) volume will be discarded, and the original glance image (the one used to create the instance, and in the resulting backup) will be later used for recovery
this may be useful for a disk-attachment strategy (where nova volumes are not supported), and you still need to recover the instance to another OpenStack, where this image doesn't exist.
Use domain-scoped authorization - depending on your use case:
single credentials with the permission to access all OpenStack authentication domains and projects -> then this toggle should be disabled, and the credentials should be provided in the only Authentication Domain tab on the left available
separate Authentication domains - then this toggle should be enabled, and all authentication domains used for authentication should be defined on the left with (+) icon
In the Authentication domain tabs (you can use your OpenStack RC file to fill these fields):
Name - name of domain
DomainI ID - optional domain ID
User/Password - OpenStack user and password
Default project - name of default project in the domain being defined
Save and run first inventory sync - this will also detect hypervisors, which may require 2 things:
assigning different node configurations to specific hosts (this must correspond with your AZ setup
providing SSH credentials (when using SSH Transfer backup strategy)
For SSH Transfer backup strategy only:
make sure you provide the correct SSH credentials for each hypervisor listed on the Hypervisors tab. You can also use SSH public key authentication.
if libvirt runs inside the container, for each host, follow this KB article.
When you want to use the Ceph RBD variant in your backup strategy:
Follow the Ceph RBD setup
Make sure to have this setup done for all nodes that will need access to the Ceph monitors
Once the volumes have appeared, assign this storage provider to the appropriate Storage (volume types) in your Hypervisor Manager details -> Storage -> your volume type -> Ceph settings:
select the provider and the corresponding storage pool
Run both full and incremental backups to verify the setup.
Instant restore setup
Node configuration
First step to initiate the configuration process for OpenStack Instant Restore service, is creating a directory that will be accessible for mounting by the NFS server. Create a specific directory on your Node machine that will be used as the target space for Instant Restore's shared resources.
Next, create an NFS share that will allow access to the /vprotect_data/ directory from other machines in the network. Sharing this directory will enable OpenStack clients to use it for virtual machine restoration.
Cinder storage backend configuration
Paths and commands may vary depending on the version of OpenStack you are using.
After creating the NFS share on the node, you need to configure the NFS backend in the cinder service. This step will allow OpenStack to access resources stored on the node via NFS. Edit the /etc/cinder/cinder.conf file and add this section at the end of the file:
Create the file you provided in the configuration as the value of nfs_shares_config parameter
and path to the NFS share:
After creating the NFS server and configuring cinder, restart the cinder volume service. Please note that the name of this service may be different depending on the OpenStack version.
Matching nodes to the OpenStack storage backends (volume types)
After completing the inventory synchronization of the OpenStack, in Node edition window you can select the storage with the NFS backend configuration. Details about the NFS backend should be supplied by the OpenStack administrator.
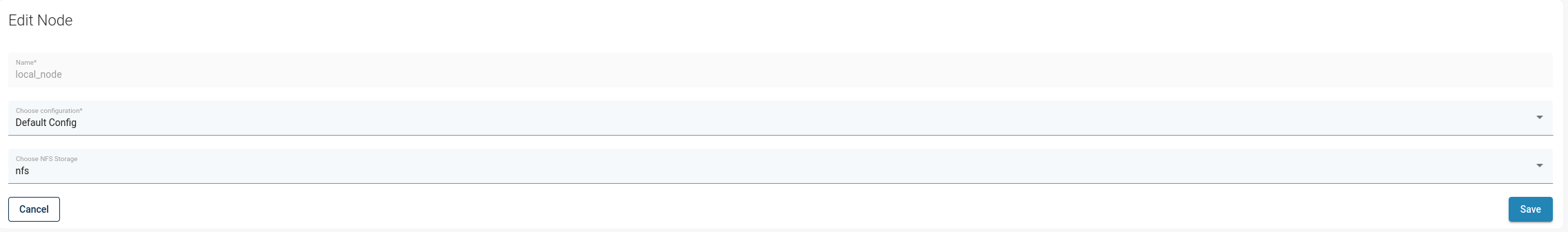
You should now be able to select "Instant restore" for backed up virtual machines.
Last updated