VMware vSphere/ESXi
Storware Backup & Recovery supports agent-less data protection for VMware vSphere and ESXi environments. Both full and incremental backups are supported.
Backup process
Full Backup
A full backup contains entire virtual machine data (and metadata) each time the backup action is executed. It is available for every guest operating system supported by VMware. At the same time, it is the most time- and resource-consuming type of backup.
Incremental Backup
Incremental backups consume less space and fewer resources than full backups because they include only the pieces of data that have changed since the last backup. Consider the following scenario, where we want to protect 3 files:
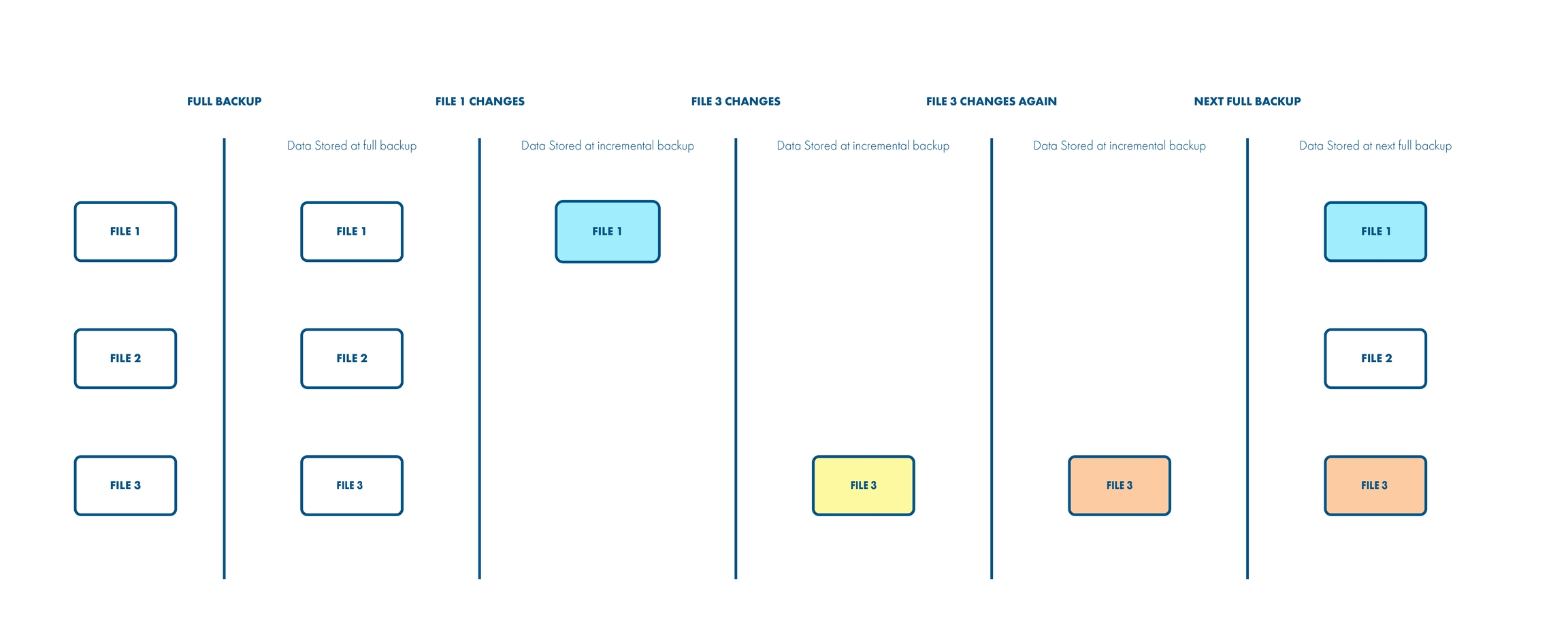
The first request for the incremental backup will always result in full backup (all data is considered as new), so all three files are backed up. At some point in time File1 changes while File2 and File3 remain untouched.
At the next execution of the backup schedule, only File1 will be backed up as it's the only one that has changed. Afterward, only File3 changes its contents, so this portion of the data will be backed up at the next scheduled backup. Again, File3 changes for the second time, which means the subsequent incremental backup will contain File3 only. Finally, the data taken at the next full backup will contain the third version of File2, the second version of File1, and the (original, unchanged) version of FIle1.
A very important thing to note here is the usage of Change Block Tracking technology, which dramatically increases performance and reduces backup time as it sends only those pieces of information that have changed at the block level. You can refer to VMware KB for a more detailed description of how CBT works.
Now that we know how we can back up our data, it is time to explain how we can transport the data to our backup destination, which brings us to the next step.
Note:
in order to execute incremental backups, you need to have at least one schedule with incremental backup selected, and only then must you execute full backup - this will result in a CBT change of the set IDs of record, which is needed for the next incremental backup.
Transport types
There are 2 transport modes supported by Storware Backup & Recovery:
Hot-Add
Network Block Device (NBD)
Transport modes are detected and selected automatically depending on the deployment configuration.
Hot-Add
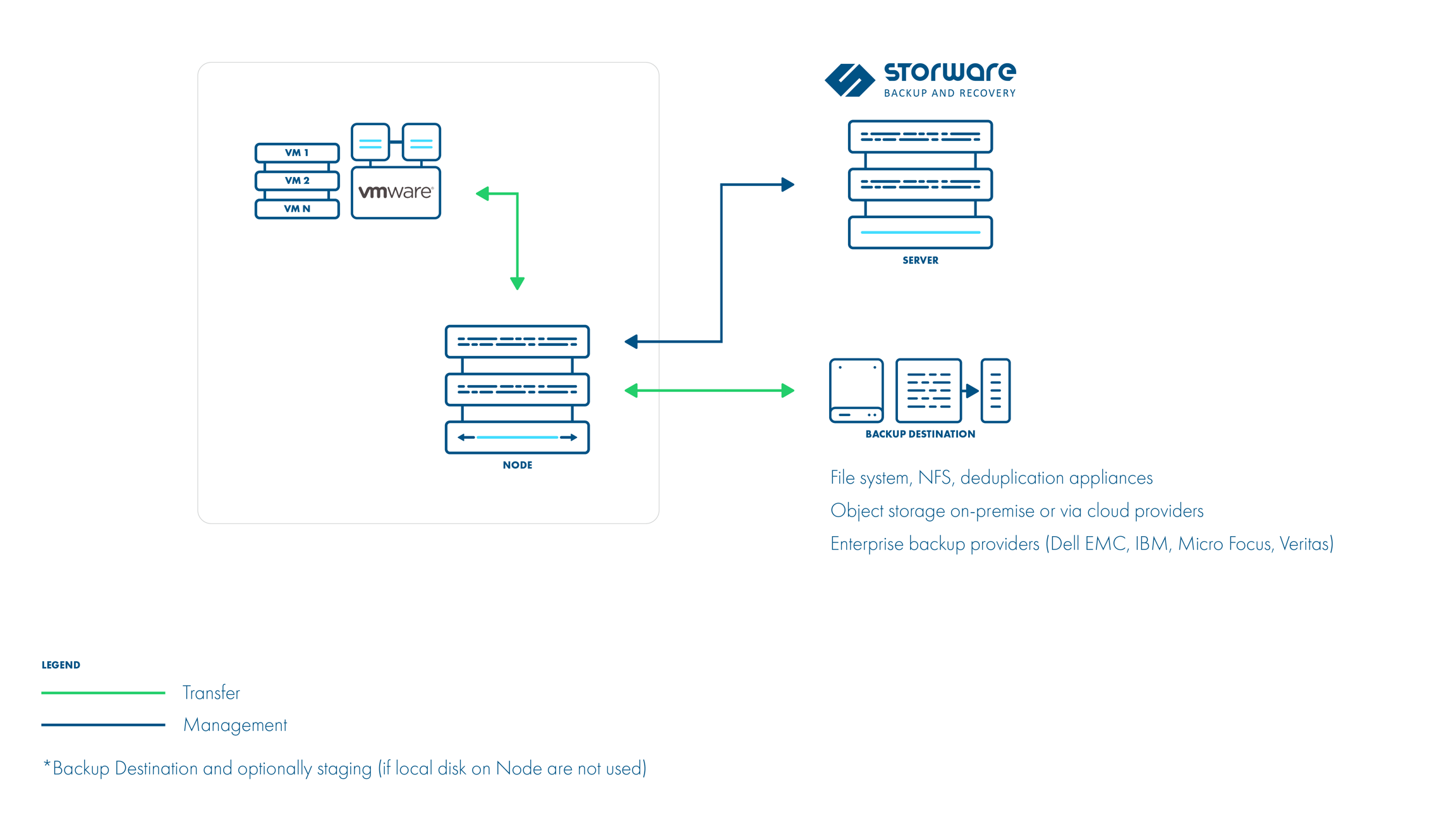
This is the default transport mode if you choose to deploy a Proxy VM (Storware Backup & Recovery Node in a VM) inside your VMware cluster. During backup, a cloned VM is created from the backup snapshot, then these disks are hot-added to our Proxy VM and transferred to the backup destination. This approach eliminates data transfer over LAN during backup and restore.
Here is an example where the Storware Backup & Recovery Server is installed anywhere in your infrastructure (accessible to the nodes) and the node is installed inside a VM in the VMware environment:
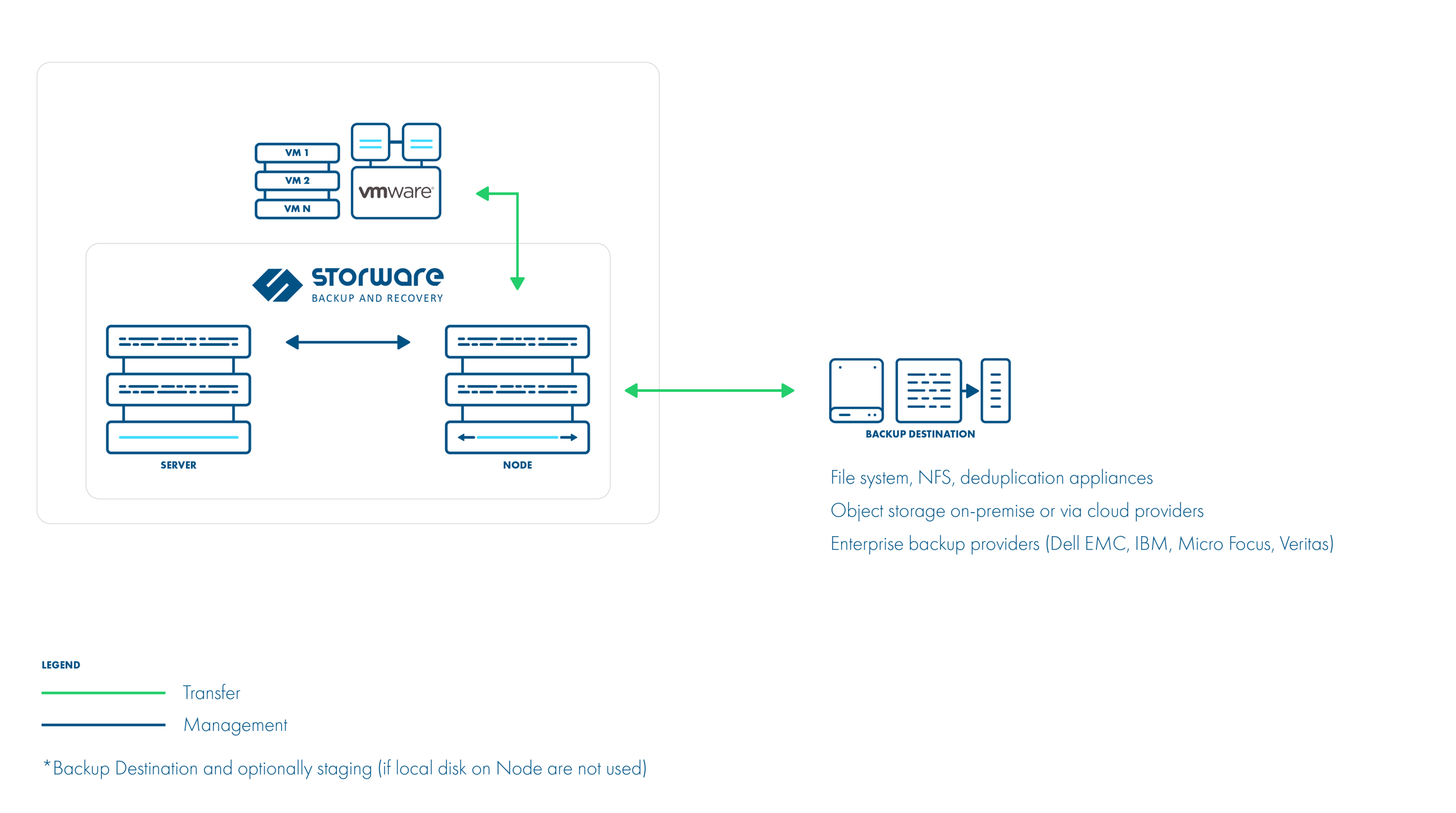
The server and node can also be installed together:
Network Block Device (NBD)
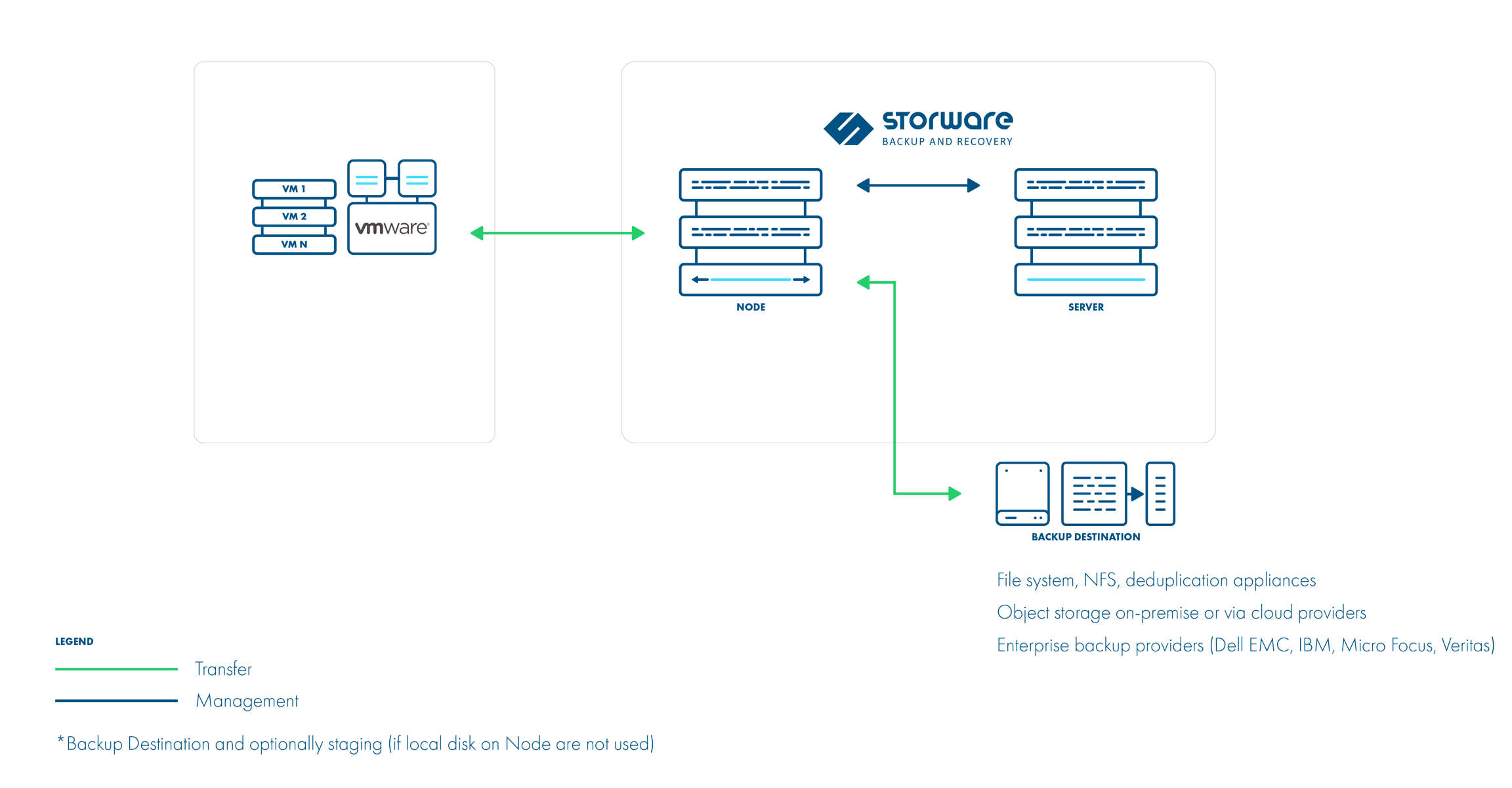
This transport mode is used when Hot-Add is not available for some reason (i.e. you decided to deploy the Node outside of the VMware environment). NBD is a Linux-style kernel module that handles remote storage as a block device and passes it over TCP/IP connection.
In this example, the Storware Backup & Recovery Server and Node are deployed outside of the VMware environment:
Note:
this transport, although simpler to set up, is not as efficient as the previous method because in this case, NBD transport is used so data will travel using LAN.
Adding a hypervisor manager
The backup user must have the following privileges for the backup/restore procedure:
VirtualMachine > Change Configuration
VirtualMachine > Edit Inventory
VirtualMachine > Provisioning
VirtualMachine > Snapshot management
Datastore > Browse datastore
Datastore > Update virtual machine files
Datastore > Update virtual machine metadata
Resource > Assign virtual machine to the resource pool
Tasks > Create task
You must have ports 443/TCP and 902/TCP open from the ESX/vCenter to the Storware Backup & Recovery node to run the backup.
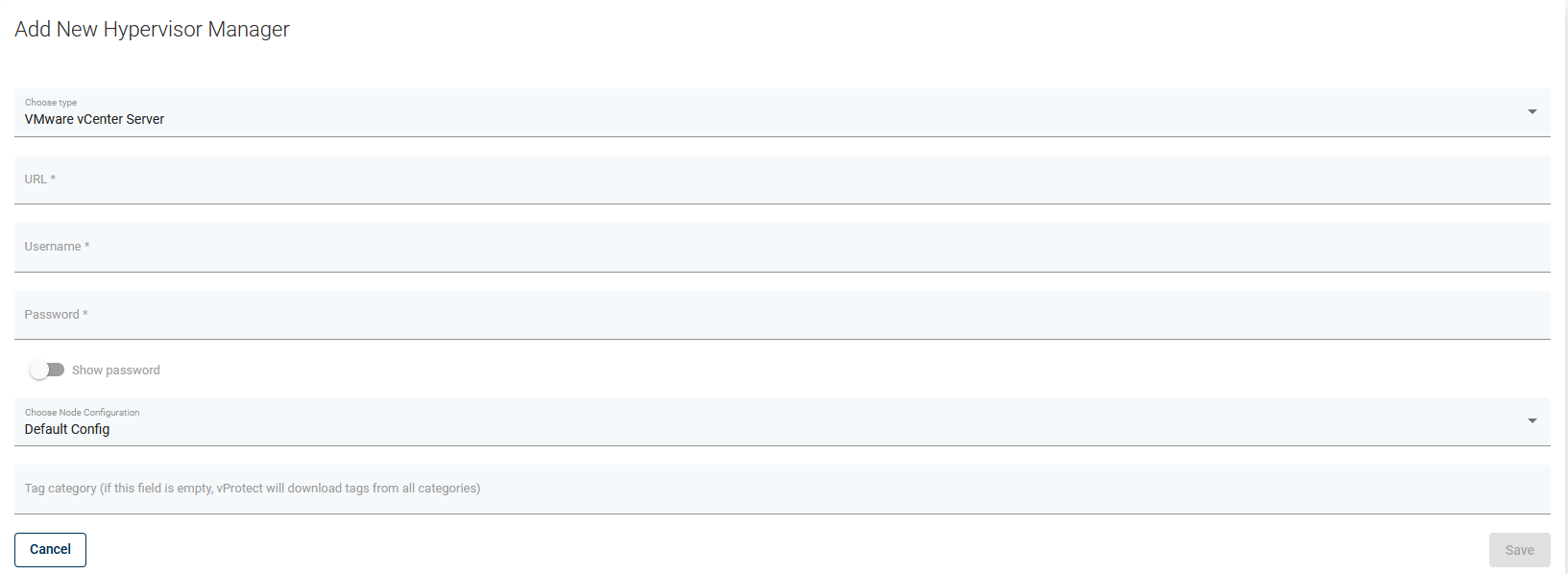
Add your vCenter as a Hypervisor Manager in the Web UI -
https://vcenter.hostname.or.ip
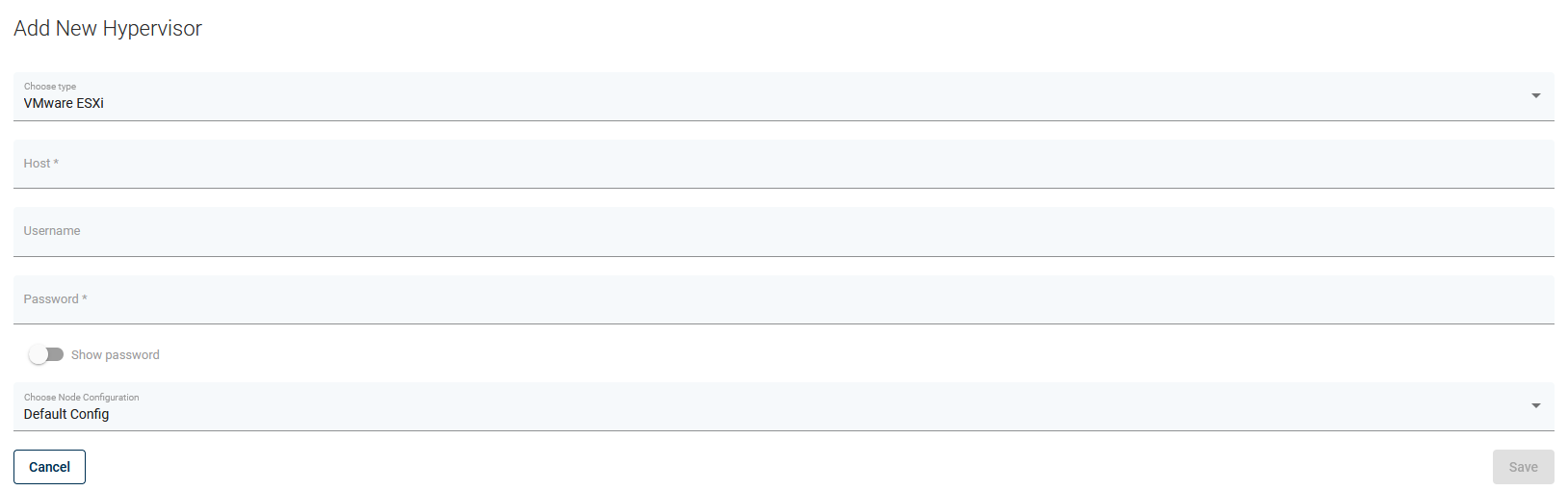
If you have stand-alone ESXi hosts - add all hypervisors separately on the Hypervisors tab - simply provide their hostnames or IPs and credentials.
Instant restore
To use an instant restore feature, backup destination from which VM will be restored, has to be of a synthetic type. The restore process creates a NFS share on the Storware Backup & Recovery node, later this share is attached to the vCenter as a new data store. Then it creates a new virtual machine and attaches the disks from the newly created data store to it.
To use instant restore you have to click the restore button in the instances list and choose the option instant restore.
Live migration
You can enable the live migration option during instant restore. It will automatically start the disks migration to the chosen storage after the VM is restored and powered on.