File Level Backup and Restore - OS Agent
Storware Backup & Recovery allows you to protect server on file level using OS Agents. This feature is available for Linux and Windows machines.
Prerequisites
Before starting, you need to install OS Agent service on a machine you want to protect. You can download the latest OS Agent installer from Storware Repository (Windows or Linux).
You need to open 15900 port on Storware Backup & Recovery Node:
firewall-cmd --add-port=15900/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --complete-reloadSupported windows platform:
Windows 10
Windows Server 2016+
Installation and registering the Agent
Linux
Install the OS Agent.
rpm -ivh sbr-osagent-x.x.x-x.el8.x86_64.rpmRun
osaccommand with register parameter on a machine where you installed OS Agent.osac -r <login> https://<host>:15900 [password]where:
login- default isadminhostis an IP address or hostname to the Storware Backup & Recovery Nodepasswordis a password of the admin user. This could be omitted but You will be prompted to type the password
Start sbr-osagent service.
systemctl start sbr-osagent
Windows
Double click on the .msi file to install the OS Agent.
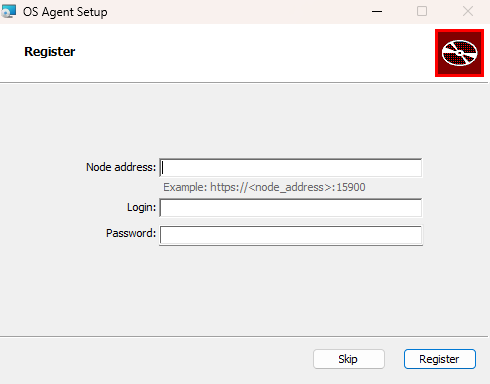
Provide necessary information when prompted:
Node addressis IP address or host name to the Storware Backup & Recovery NodeLogin- default isadminPasswordis password of admin user.
Define Backup SLAs
To define a Backup SLA, You need to provide rules:
include (mandatory)
exclude (optional)
The Agent process files by include rules and then by exclude rules. The Agent scan filesystem using include rules. If any file is matched, it will be processed by exclude rules, if exists. When exclude rules match file, it will be omitted, if not it will be backed up.
The rule is defined by:
Directory pattern
File name patterns - this could have multiple values
Directory pattern should provide a path to the filesystem. You could also set Recursive attribute. When this attribute is set, scanning will be recursive and follow deeper with directory structure. If not only files and folders (without content) will be matched. For Windows, You should use \ character as a folder delimiter. For Linux, You should use / character.
File name pattern should provide a pattern to match the file on the filesystem. This could be any file when * is provided or part of the name like extension *.pdf. Additional matching patterns are provided below. When multiple patterns are provided, if any is matched then next will not be checked. Patterns can be separated by commas.
All rules could be used as include or exclude rule. All characters provided for Windows are case insensitive, for Linux are case sensitive.
Additional pattern matchings
For better matching You could provide some more accurate patterns:
* - any of character
? - only one or zero characters
** - recursive (only for directory pattern)
To better understand how it works, check the examples:
Examples for directories
C:\Users\*\Desktop (for Windows) /home/*/Desktop (for Linux) - this will backup any users desktop directory, where * match all names
C:\Users\?oo\Desktop (for Windows) /home/?oo/Desktop (for Linux) - this will backup users directory when first letter of name is any character and rest name should ends with oo (foo, goo, etc.)
C:\**\logs (for Windows) /**/logs (for Linux) - this will backup logs catalog that exists anywhere in the path. This means path should start from C:\ or / then any folder or subfolder (**) and next folder should be named logs
We also could mix all patterns:
C:\**\?ogs\**\a?c (for Windows) or /**/?ogs/**/a?b (for Linux) - this means path should start from C:\ or / then any folder or subfolder (*) and next folder name should start with any character and rest should be ogs (logs, dogs, etc.) then any folder or subfolder (*) and next folder name should start with letter a then could exists only one character and ends with c letter (abc, ac, etc.)
Example for files
*.txt - only txt files
.* - hidden files for Linux
a?c - file that start with letter a then could exists one character then b letter (ac, abc, eg.)
Backup using VSS (Windows only)
For Windows, the OS Agent can create a backup using a filesystem snapshot. Before the backup begins, a disk snapshot is created. The OS Agent uses this snapshot to read all files and releases it once the backup is complete.
If some problems occur while making a snapshot, the user could choose how the Agent should behave:
Fail backup - the backup task is immediately finished and fails the task.
Use a regular copy - the backup is switched to a regular file copy and continue.
Use a regular copy with a warning - the backup is switched to a regular file copy and continues. A warning will be displayed when the task is completed.
This setting can be changed in Agents -> Backup Policies -> edit policy -> Backup process tab.
Archiving the OS Agent
OS Agent can be archived by clicking button “Archive” on the agent instances list or in the agent details view. Archived agents can't be backed up any more. The only available actions for archived agents are “Restore”, “Download” and “Delete”. Agent can not be unarchived.
Limitations
If the backup destination is configured on Data Domain, it is recommended to use local disk as staging space.
Symlinks are not supported.
Up to five million protected objects per OS agent instace